Ranking Poker Hands Python
How can I speed up my Python poker hand vs. hand equity calculator
- Ranking Poker Hands Python Tutorial
- Ranking Poker Hands Python Games
- Ranking Poker Hands Python Game
- Ranking Poker Hands Python Cheat
poker calculator
5-card poker hand calculator
holdem_calc
pokerstars odds calculator
poker hand scenarios
poker odds chart
poker equity calculator app
Poker Hand Combinations Explained. Poker hands fall into one of ten categories. The highest is a royal flush, followed by a straight flush, then four of a kind, a full house, a flush, a straight. In this article, I showed how to represent basic poker elements (e.g. Hands and Combos) and how to calculate poker odds assuming random hands as well as ranges in Python while telling a true history of a night at the Venetian. We showed how exciting (and probabilistically interesting) poker can be.
First a disclaimer: I am a medical professional who plays with both Python and poker as a hobby. I have no formal training in neither of those and I am not aware of what is in the curriculum of a computer science class.The computer that I use is a desktop i7-4790 3.6 Ghz with 16 GB of RAM along with Jupyter Notebooks.
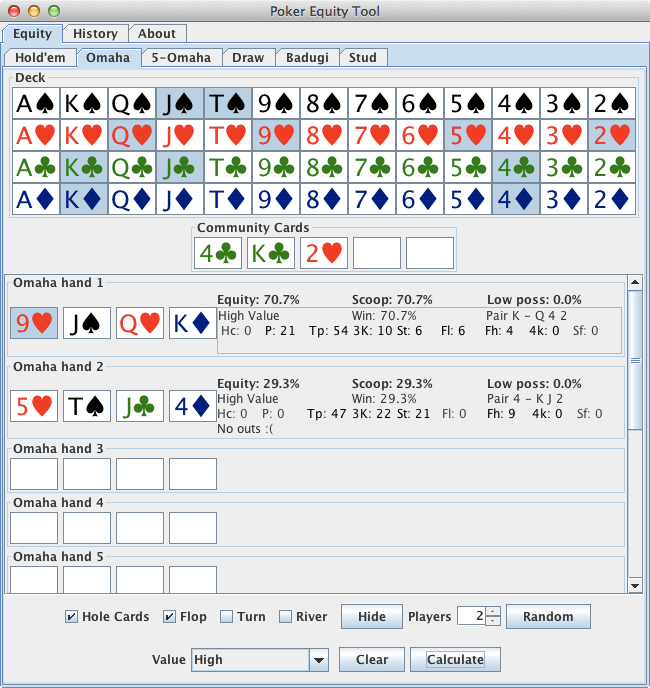
My goal was to code the equivalent of pokerstrategy.com Equilab or https://www.cardschat.com/poker-odds-calculator.php for me. I would stick to Texas Holdem only.
In order to to that I needed to code an evaluator for any 5 card combination.I did that and it does the job perfectly, considers every card in a hand and produces a tuple as an output, for example:
So it differentiates between A 9 8 7 3 and A 9 8 7 5 flush or high-hand. I checked with theoretical number of royal flushes, quads, full houses etc. over all 2 598 960 card ccombinations and the frequencies check out (https://www.quora.com/How-many-possible-hands-are-there-in-a-five-card-poker-game)
Ranking Poker Hands Python Tutorial
Now I tried to evaluate every possible 5-card combination out of those 2.6 millions and it took disappointing 51 seconds.
I kind of expected that thinking my 5-card evaluator can't be the champion of algorithm competitions and surely there is a better way to do it (I can post it here if it is of relevance), but I thought never mind. Once all 5-card combinations are evaluated I will save them in a dictionary and next time I will load the dictionary and when I have any 5-card combination I will simply look up the result.
Another disappointment. 10 000 000 (10 million) board searches takes approx. 23-24 seconds.This is a a part that I do not understand!!!I have basically a database that has 2.6 mil. rows x 2 columns and the search is SO PROHIBITIVELY slow. How do then billion record databases get anything accomplished?My whole dictionary when saved to a file takes 88 Mb - is that a HUGE database?
And finally I made a full hand vs. hand evaluator that in pseudo-code does this:
Given 2 hands, for example AhAs vs. 6d6h
list all boards that can be dealt with those 2 'dead' cards, which is 1 712 304 boards
list all 21 combinations of hand1 with board 1,
search the ranked_hands dictionary with those 21 combinations and return the best possible outcome (21 combinations because in texas holdem you can use one, two or no cards from your hand with any of the 5 community cards on board)
do the same with hand2 and board1
compare best outcome of hand1 with best outcome of hand2
count if the outcome favours hand1, hand2 or if it is a tie
go to next board
Ranking Poker Hands Python Games
This algorithm does approximately 71 million dictionary lookups - each of 1.7 million boards x 42 (every hand's 21 combinations twice).
Now, THIS IS A DISASTER. Approximately 80 seconds per hand vs. hand matchup.With those speeds there is nothing I can begin.So, any input would be appreciated as to how I can make this better?
Is it me and my lack of proper computer science and algorithm knowledge?
Is it Python?Is it Jupyter Notebooks inside of Chrome?
Any other suggestions?

Code as requested:
Maybe one print(total) to many but was originally in Jupyter Notebook
[Python 3] Holdem Hand v Hand Equity Calculator :confused , This simple method misses draws but is still accurate enough for my applications. If I (or anyone here) can speed this up substantially, in the� Once again, I’ll use an equity calculator to determine Hero’s equity. In this case, Hero’s hand has 35.84% equity vs. Villain’s range. Now you can create variables for EstFoldPercent and Equity. Hand2_Fold_Percent = .10 Hand2_Equity = .3584 Now plug the variables for this hand into the AllinExpectedValue function, and print the results.
You could use the dbm module (see https://docs.python.org/3/library/dbm.html) , or bsddb in python 2.x, to store your entire lookup table in a database file, if it's too large to fit in memory in a dict. Then it might take some time to fill out the table, but you'd only need to do that once.
#1 Poker Odds Calculator Online 2020, The #1 Ranked Poker Odds Calculator by CardsChat™ - Easy & FREE tool for As a professional poker player it is important to review hands and be aware of equity calculations. You can fill in your own hand and calculate the chances of you winning To get you up to speed, here's a quick rundown of hand order. The hackerrank question asked me to write a program that would determine the best poker hand possible in five-card draw poker. We are given 10 cards, the first 5 are the current hand, and the second 5 are the next five cards in the deck. We assume that we can see the next five cards (they are not hidden).
ktseng/holdem_calc: Texas Hold'em Odds Calculator, GitHub is home to over 50 million developers working together to host and review code, also shows how likely each set of hole cards is to make a certain poker hand. python holdem_calc.py Ad Kd Qc Qs Winning Percentages: (Ad, Kd) hands in a single run, the user has the choice to allow Holdem Calculator to read � To calculate your poker equity - or how often you should win a hand, you can use a simple formula. Count how many outs you have. For example, if you're drawing to a flush, you have 13 suited cards, two in your hand, two on the board - leaves 9 outs.
julianandrews/pyeval7: Python Texas Hold'em hand evaluation and , Python Texas Hold'em hand evaluation and equity calculation library - julianandrews/pyeval7. poker hand evaluator and range equity calculator with a clean native python interface and all performance critical parts implemented in Cython. If there isn't a wheel for your package, feel free to open an issue on GitHub. Calculate your equity with the PokerStrategy.com Equilab. Our software tool gives you the ability to analyse the equity against a specific hand or against a range of hands. On top of that, you can also check your equity in any given scenario, thanks to the various filters you can use. What is equity?
How to Calculate Poker Probabilities in Python, hand to construct my hand. I do not remember exactly what happened pre-flop and what my position was. However, I do� How can I speed up my Python poker hand vs. hand equity calculator First a disclaimer: I am a medical professional who plays with both Python and poker as a hobby. I have no formal training in neither of those and I am not aware of what is in the curriculum of a
Approximating Poker Probabilities with Deep Learning, Many poker systems, whether created with heuristics or machine learning, rely 2 22We implemented a na�ve hand evaluator in python. to calculate all the features in the input vector which is a speed-up of ∼600x holding your hole cards (two cards in your hand) and the current board cards constant. Both when determining your final poker hand and the poker hand that wins the pot. Figuring Out Your Hand: In Texas Hold'em your final best 5-card hand can use both your hole cards (the two cards dealt to you face down at the beginning of the hand), one of your hole cards or none of your hole cards to make up your final hand.
Comments
- Where's the code?
- Perhaps better suited to Code Review although they'll require code to review.
- I'd be interested to see and review the code but might be better on Code Review as pointed out by @Sayse as this is very broad for a SO question. If you choose to post on CR please link here and I'll take a look. Using a dictionary is often a good idea for these kind of combinatorics problems but it sounds like in your case you have a dictionary which is not especially usefully structured.
- Sorry. I wasn't aware that there are different platforms for asking different questions, lilke StackOverflow and Code Review. As said, a hobbyist. Code added.
- @ rioZg I added a comment on my answer with some run times for this algorithm using multiprocessing Python and Go.
- That was my initial idea but if you look at the link in the original question to Quora statitistics page you will see that a very small minority of hands constitute anything else but 'nothing' and 'one pair' and for those hands you need complete evaluation down to last kicker. So I thought any 'shortcut' would be more work than it was worth.
- @rioZg having so few playable hands out the set of all possible hands is exactly the thing that makes it advantageous to do this computation on-the-fly. All that is needed is to code some functions that will determine if their input matches a certain pattern, and then return the details (probably suit/high card) needed to assign a numerical score to the input. Even better: there are only 8 cases that all playable hands will fall into, and they are all easy to express in Python code. I think if you try this approach you'll find it is a very straightforward solution.
- No need to evaluate any given hand past those 8 special cases: if a hand doesn't fall into one of them, it is automatically a zero score.
- Not true Z4-tier. The board is 9 8 7 3 2 , one player holds A6 the other A4, the best possible hand for player 1 is A 9 8 7 6, for player 2 A 9 8 7 4, player 1 wins on the last kicker. The board is As 3s 4s 5s Qd , player1 is holding 2s2d, player 2 is holding KsKd, player 3 is holding 8s7s, you need more than just player 2 has flush, player 3 has flush because player 2 beats player 3 but loses to player one who has straight flus. So knowing that hand is zero score is not sufficient.
- I just updated this answer with a working example that should work for any hand. It first assigns a hand to a category (ie. SF, FH, 3K, etc...) and then maintains a list of the cards that can be used to determine the relative order of 2 hands within the same category. This takes advantage of the fact that tie breakers follow the same algorithm regardless of the hand category; the only thing that changes are the specific cards that are compared. Variants of this problem are frequently used in programming competitions.
- ...hand vs. hand or range equity is the essential tool in every players toolbox. You are doing it almost in every hand you get involved in.
- Ok, I don't really know anything about poker but I thought as your hand is only visible to you then hand Vs hand is more of an academic exercise than an in-play tool.
- Thanks for the link. Very useful. But it seems to be above my competence level especially given that all are in programming languages not familiar to me so I can not easily evaluate how they did it. But if they managed 15-16 million evaluations per second on old computers in 2006. that would be very acceptable to me. Full evaluation of hand vs. hand on all possible boards is around 72 million evaluations.
- I have to admit that I haven't got my head round it yet either but it's enough to convince me that we're not going to get easy improvements in your existing algorithm. It's looks like a very elaborate system of lookups optimised to take advantage of the exact characteristics of poker hands. Having said that you could probably get your existing algorithm quite a bit faster if you optimised it for multiprocessing (Python only uses one CPU thread by default) and/or used a faster language. I love Python but if you are looking for fastest possible execution it's far from the best choice.
- Thanks SimonN. It occured to me through looking for the solution that leaving Python for 'greener pastures' might be the only solution.
Hot Questions
Below is the complete guide for determining how to rank various poker hands. This article covers all poker hands, from hands in standard games of poker, to lowball, to playing with a variety of wild cards. Scroll to the end to find an in-depth ranking of suits for several countries, including many European countries and North American continental standards.
Standard Poker Rankings
A standard deck of cards has 52 in a pack. Individually cards rank, high to low:
Ace, King, Queen, Jack, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2
In standard poker (in North America) there is no suit ranking. A poker hand has 5 cards total. Higher ranked hands beat lower ones, and within the same kind of hand higher value cards beat lower value cards.
#1 Straight Flush
In games without wild cards, this is the highest ranking hand. It consists of five cards in sequence of the same suit. When comparing flushes, the hand with the highest value high card wins. Example: 5-6-7-8-9, all spades, is a straight flush. A-K-Q-J-10 is the highest ranking straight flush and is called a Royal Flush. Flushes are not permitted to turn the corner, for example, 3-2-A-K-Q is not a straight flush.
#2 Four of a Kind (Quads)
A four of a kind is four cards of equal rank, for example, four jacks. The kicker, the fifth card, may be any other card. When comparing two four of a kinds, the highest value set wins. For example, 5-5-5-5-J is beat by 10-10-10-10-2. If two players happen to have a four of a kind of equal value, the player with the highest ranking kicker wins.
#3 Full House (Boat)
Ranking Poker Hands Python Game
A full house consists of 3 cards of one rank and 2 cards of another. The three cards value determines rank within Full Houses, the player with the highest rank 3 cards wins. If the three cards are equal rank the pairs decide. Example: Q-Q-Q-3-3 beats 10-10-10-A-A BUT 10-10-10-A-A would beat 10-10-10-J-J.
#4 Flush
Any five cards of the same suit. The highest card in a flush determines its rank between other flushes. If those are equal, continue comparing the next highest cards until a winner can be determined.
#5 Straight
Five cards in sequence from different suits. The hand with the highest ranking top card wins within straights. Ace can either be a high card or low card, but not both. The wheel, or the lowest straight, is 5-4-3-2-A, where the top card is five.
#6 Three of a Kind (Triplets/Trips)
A three of a kind is three card of equal rank and two other cards (not of equal rank). The three of a kind with the highest rank wins, in the event they are equal, the high card of the two remaining cards determines the winner.
#7 Two Pairs
A pair is two cards that are equal in rank. A hand with two pairs consists of two separate pairs of different ranks. For example, K-K-3-3-6, where 6 is the odd card. The hand with the highest pair wins if there are multiple two pairs regardless of the other cards in hand. To demonstrate, K-K-5-5-2 beats Q-Q-10-10-9 because K > Q, despite 10 > 5.
#8 Pair
A hand with a single pair has two cards of equal rank and three other cards of any rank (as long as none are the same.) When comparing pairs, the one with highest value cards wins. If they are equal, compare the highest value oddball cards, if those are equal continue comparing until a win can be determined. An example hand would be: 10-10-6-3-2
#9 High Card (Nothing/No Pair)
If your hand does not conform to any of the criterion mentioned above, does not form any sort of sequence, and are at least two different suits, this hand is called high card. The highest value card, when comparing these hands, determines the winning hand.
Low Poker Hand Ranking
In Lowball or high-low games, or other poker games which lowest ranking hand wins, they are ranked accordingly.
A low hand with no combination is named by it’s highest ranking card. For example, a hand with 10-6-5-3-2 is described as “10-down” or “10-low.”
Ace to Five
The most common system for ranking low hands. Aces are always low card and straights and flushes do not count. Under Ace-to-5, 5-4-3-2-A is the best hand. As with standard poker, hands compared by the high card. So, 6-4-3-2-A beats 6-5-3-2-A AND beats 7-4-3-2-A. This is because 4 < 5 and 6 < 7.
The best hand with a pair is A-A-4-3-2, this is often referred to as California Lowball. In high-low games of poker, there is often a conditioned employed called “eight or better” which qualifies players to win part of the pot. Their hand must have an 8 or lower to be considered. The worst hand under this condition would be 8-7-6-5-4.
Duece to Seven
The hands under this system rank almost the same as in standard poker. It includes straights and flushes, lowest hand wins. However, this system always considers aces as high cards (A-2-3-4-5 is not a straight.) Under this system, the best hand is 7-5-4-3-2 (in mixed suits), a reference to its namesake. As always, highest card is compared first. In duece-to-7, the best hand with a pair is 2-2-5-4-3, although is beat by A-K-Q-J-9, the worst hand with high cards. This is sometimes referred to as “Kansas City Lowball.”
Ranking Poker Hands Python Cheat
Ace to Six
This is the system often used in home poker games, straights and flushes count, and aces are low cards. Under Ace-to-6, 5-4-3-2-A is a bad hand because it is a straight. The best low hand is 6-4-3-2-A. Since aces are low, A-K-Q-J-10 is not a straight and is considered king-down (or king-low). Ace is low card so K-Q-J-10-A is lower than K-Q-J-10-2. A pair of aces also beats a pair of twos.
In games with more than five cards, players can choose to not use their highest value cards in order to assemble the lowest hand possible.
Hand Rankings with Wild Cards
Wild cards may be used to substitute any card a player may need to make a particular hand. Jokers are often used as wild cards and are added to the deck (making the game played with 54 as opposed to 52 cards). If players choose to stick with a standard deck, 1+ cards may be determined at the start as wild cards. For example, all the twos in the deck (deuces wild) or the “one-eyed jacks” (the jacks of hearts and spades).
Wild cards can be used to:
- substitute any card not in a player’s hand OR
- make a special “five of a kind”
Five of a Kind
Five of a Kind is the highest hand of all and beats a Royal Flush. When comparing five of a kinds, the highest value five cards win. Aces are the highest card of all.
The Bug
Some poker games, most notably five card draw, are played with the bug. The bug is an added joker which functions as a limited wild card. It may only be used as an ace or a card needed to complete a straight or a flush. Under this system, the highest hand is a five of a kind of aces, but no other five of a kind is legal. In a hand, with any other four of a kind the joker counts as an ace kicker.
Wild Cards – Low Poker
During a low poker game, the wild card is a “fitter,” a card used to complete a hand which is of lowest value in the low hand ranking system used. In standard poker, 6-5-3-2-joker would be considered 6-6-5-3-2. In ace-to-five, the wild card would be an ace, and deuce-to-seven the wild card would be a 7.
Lowest Card Wild
Home poker games may play with player’s lowest, or lowest concealed card, as a wild card. This applies to the card of lowest value during the showdown. Aces are considered high and two low under this variant.
Double Ace Flush
This variant allows the wild card to be ANY card, including one already held by a player. This allows for the opportunity to have a double ace flush.
Natural Hand v. Wild Hand
There is a house rule which says a “natural hand” beats a hand that is equal to it with wild cards. Hands with more wild cards may be considered “more wild” and therefore beat by a less wild hand with only one wild card. This rule must be agreed upon before the deal begins.
Incomplete Hands
If you are comparing hands in a variant of poker which there are less than five cards, there are no straights, flushes, or full houses. There is only four of a kind, three of a kind, pairs (2 pairs and single pairs), and high card. If the hand has an even number of cards there may not be a kicker.
Examples of scoring incomplete hands:
10-10-K beats 10-10-6-2 because K > 6. However, 10-10-6 is beat by 10-10-6-2 because of the fourth card. Also, a 10 alone will beat 9-6. But, 9-6 beats 9-5-3, and that beats 9-5, which beats 9.
Ranking Suits
In standard poker, suits are NOT ranked. If there are equal hands the pot is split. However, depending on the variant of poker, there are situations when cards must be ranked by suits. For example:
- Drawing cards to pick player’s seats
- Determining the first better in stud poker
- In the event an uneven pot is to be split, determining who gets the odd chip.
Typically in North America (or for English speakers), suits are ranked in reverse alphabetical order.
- Spades (highest suit), Hearts, Diamonds, Clubs (lowest suit)
Suits are ranked differently in other countries/ parts of the world:
- Spades (high suit), Diamonds, Clubs, Hearts (low suit)
- Hearts (high suit), Spades, Diamonds, Clubs (low suit) – Greece and Turkey
- Hearts (high suit), Diamonds, Spades, Clubs (low suit) – Austria and Sweden
- Hearts (high suit), Diamonds, Clubs, Spades (low suit) – Italy
- Diamonds (high suit), Spades, Hearts, Clubs (low suit) – Brazil
- Clubs (high suit), Spades, Hearts, Diamonds (low suit) – Germany
REFERENCES:
http://www.cardplayer.com/rules-of-poker/hand-rankings
https://www.pagat.com/poker/rules/ranking.html
https://www.partypoker.com/how-to-play/hand-rankings.html